Young children have weaker immunity, so they are more likely to catch viruses and bacteria. Toddlers who have frequent contact with peers in nursery or kindergarten and do not follow hygiene rules are particularly vulnerable to illness: they often use the same cups, play while coughing and sneezing on each other. Most childhood diseases are transmitted through droplets, i.e. on dirty hands, toys or through viruses found in exhaled air.
What can a child bring from kindergarten?
The most common diseases that children transmit to each other are infections such as colds or flu. The viruses that cause these diseases run rampant mainly in the fall and winter and can decimate entire groups. Another group of preschool ailments are infectious diseases of childhood. Many of them can be vaccinated against, which is why they occur less and less often, but some of them are making a comeback because some parents choose not to vaccinate them. Doctors recommend that children who are most at risk of infectious diseases be vaccinated on schedule. Many infectious diseases of childhood are considered mild, but their complications, such as dehydration from rotavirus or pneumonia from chickenpox, can be serious.
The most common infectious diseases of childhood
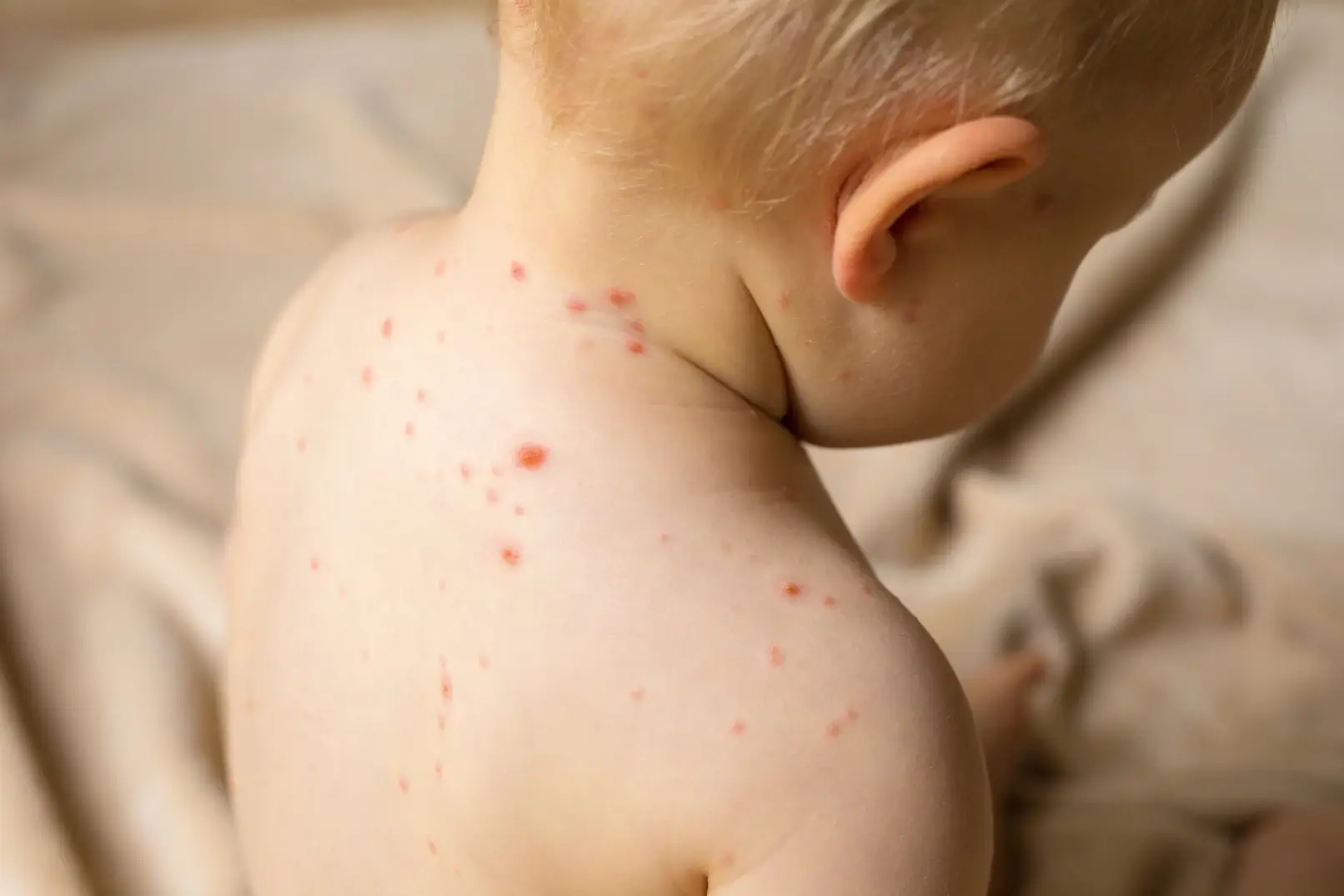
- Chickenpox – peak incidence occurs in February and March. The incubation period of the varicella virus is 17-21 days; the disease is contagious from the day before the vesicles appear until the scabs fall off. Symptoms of chickenpox include small fluid-filled blisters that appear all over the body and are very itchy. The blisters turn into scabs and fall off after about 2-3 weeks. During the illness there is high fever and loss of appetite. Vaccination against chickenpox is not mandatory, but it is reimbursed for children who attend nursery, although chickenpox is also common among school-age children.
- Rotavirus – an infectious disease caused by a virus. It is one of the most common causes of hospitalization in young children because it leads to dehydration, which can be life-threatening. The incubation period for this highly contagious virus is 1-3 days. Symptoms of rotavirus infection include diarrhea, watery stools, vomiting and abdominal pain. The disease is often accompanied by fever, weakness and malaise. Rotavirus vaccination has recently been included inthe mandatory vaccination schedule.
- Bostonka – a viral infectious disease, common in autumn and spring. Preschool-age children are most often ill. Its incubation period is 3-4 days. Boston disease is characterized by a vesicular rash that turns into ulcers that appears first on the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat, then on the hands and feet. The rash is accompanied by fever, malaise, and nausea.
- Measles – a viral disease that is almost non-existent in Poland thanks to vaccinations – does appear in Ukraine. The incubation period for measles is 9-11 days. At the beginning of the illness, the child has a high fever, a dry cough, and symptoms of pharyngitis and conjunctivitis. After 3-4 days, white spots with a red border appear on the mucous membrane of the cheeks, then gradually from above, a characteristic rash appears over the whole body: thick spots, peeling off towards the end of the infection. The disease is accompanied by high temperature, complications are possible: inflammation of the brain, pneumonia, bronchi, laryngitis.
- Rubella – eliminated by vaccination. It is not dangerous for the baby, only for pregnant women. The incubation period is 14 to 21 days – an infected person is contagious for 7 days before and after the appearance of the rash, which is pale pink, fine and confluent. Spots are visible behind the ears, then the rash appears on the face and trunk and on the limbs. Rubella is accompanied by a rise in temperature and enlarged lymph nodes. The rash does not cause itching.
- Mumps – rare due to mandatory vaccination. Mumps is an inflammation of the parotid glands. The incubation period is 14-21 days, but you can become infected 9 days before and after the onset of symptoms. A child with mumps has a fever, nausea, and painful, severe swelling behind the ears. Mumps causes complications because the virus attacks other organs, including the thyroid, ovaries, and testicles. Therefore, mumps, although a mild disease, can be dangerous for boys.
- Whooping cough – an infectious disease caused by bacteria, eliminated by vaccination, but recently making a comeback, especially in adults. It resembles a respiratory infection – it manifests itself with a dry cough and elevated temperature. Then shortness of breath and coughing fits with expectoration of sticky sputum appear. The incubation period lasts from 3-4 days to 2 weeks, but the patient is contagious until the cough stops. The disease is treated with antibiotics.
- Scarlet fever – a bacterial disease resembling strep throat. Infection occurs through droplets. The first symptoms are redness, severe sore throat and high temperature. A rash appears: fine and confluent, visible on the chest and neck, which then spreads over the entire body, in the bends of the elbows and knees and on the face (without the triangle between the nose, mouth and chin). After a few days, the baby’s tongue turns “raspberry” – red lumps appear on it. Incubation period: 1 to 5 days after infection.